ELISA
ELISA (ELectrostatIc Storage ring for ions, Aarhus) was built in 1998 as the first electrostatic storage ring in the world. It has since been copied, and several electrostatic storage rings have been constructed in Japan, Germany and Sweden.
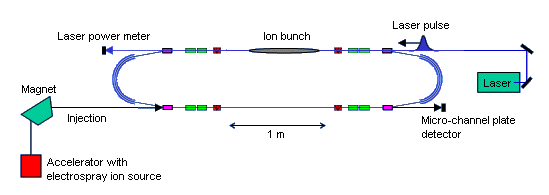
Schematic Diagram of ELISA
ELISA enables storage of low-energy ions for extended periods of time. It allows interaction of the stored ions with laser light and low-energy electrons for studies in photo-, bio-, cluster and molecular physics.
ELISA complements the magnetic storage ring ASTRID, where ions can be stored at much higher energies.
Parameters of ELISA:
Parameter |
Value |
| Highest storage energy | 22 keV/charge |
| Average pressure | <10-11 mBar |
| Circumference | 7.6 m |
| Storage time | tens of s up to minutes |
160° spherical deflectors |
|
| Electrode radii | 235 and 265 mm |
| Nominal voltages | ±3.25 kV |
10° deflectors |
|
| Plate distance | 50 mm |
| Plate length | 100 mm |
| Nominal voltages | ± 2.4 kV |
Electrostatic Quadrupoles |
|
| Inscribed radius | 26.2 mm |
| Electrode length | 50 mm |
| Nominal voltages | ± 0.37 kV |

ELISA is used by several groups in the Department of Physics and Astronomy. You can read more about ELISA and the research carried out at the following links.
- https://phys.au.dk/forskning/forskningsomraader/atomar-molekylaer-og-optisk-fysik/molecular-physics/
You can read more about ELISA here:
- Design and first operation of the Electrostatic Storage Ring, ELISA
- Operational experience with the Electrostatic Storage Ring, ELISA
- Intensity limitation of the the Electrostatic Storage Ring, ELISA
For further information contact
Last Modified 16 December 2024